- Home
-
PHOTO 1
-
PHOTO 2
-
PHOTO 3
- INFO >
- CLASS NOTES
-
ASSIGNMENTS
>
- STUDIO LIGHTS
- Composing: Creating an Abstract or Geometric Composition
- Composing: Creating an Abstract or Geometric Composition
- EMPHASIS ON COLOR THEORY
- DESIGNING IN B&W
- Formal and Informal Portraits
- CUBIST PORTRAITS
- NATURAL LIGHTING
- COMPOSITION - SCAVENGER HUNT
- STREET PHOTOGRAPHY
- MANDALA
- NIGHT
- RHYTHM & REPETITION
- PATTERNS & RHYTHM WITH LIGHT
- STUDIO PORTRAITURE
- PHOTOGRAM - MEMOIRS - THE DIGITAL VERSION
- HDR Landscapes
- PORTFOLIO
- VIDEOS
- HANDOUTS
- GALLERY
-
AP 2D ART + DESIGN
- INFO >
- SUMMER PROJECT
- SUSTAINED INVESTIGATION
- ELEMENTS + PRINCIPLES
- STUDIO LIGHTS
-
ASSIGNMENTS
>
- DESIGNING IN B&W
- COLOR THEORY
- TRIPTYCH
- SUSTAINED INVESTIGATION #1
- SUSTAINED INVESTIGATION #2
- SUSTAINED INVESTIGATION #3
- SUSTAINED INVESTIGATION #4
- SUSTAINED INVESTIGATION #5
- SUSTAINED INVESTIGATION #6
- SUSTAINED INVESTIGATION #7
- SUSTAINED INVESTIGATION #8
- SUSTAINED INVESTIGATION #9
- SUSTAINED INVESTIGATION #10
- ABSTRACT & GEOMETRIC COMPOSITION
- STUDIO PORTRAITURE
- TEXTURES & ABSTRACTIONS FROM THE...
- WEBSITE PORTFOLIO
- CLASS NOTES
- HANDOUTS
- VIDEOS
- GALLERY
- 3D ART 1
- 3D ART 2
- 3D ART 3
- Contact
GLOBAL PREHISTORY
(40,000 - 500 B.C.E.)
|
CONTENT: What do you see?
FORM: The details (what you see more exactly). How the artist delivers the content. CONTEXT: Everything NOT observable. FUNCTION: The intended purpose of the work. APAH 250 IMAGES1. Apollo 11 stones
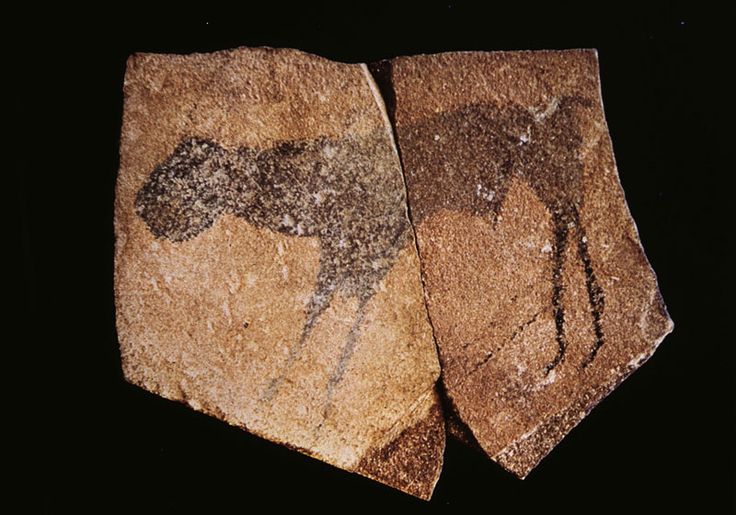
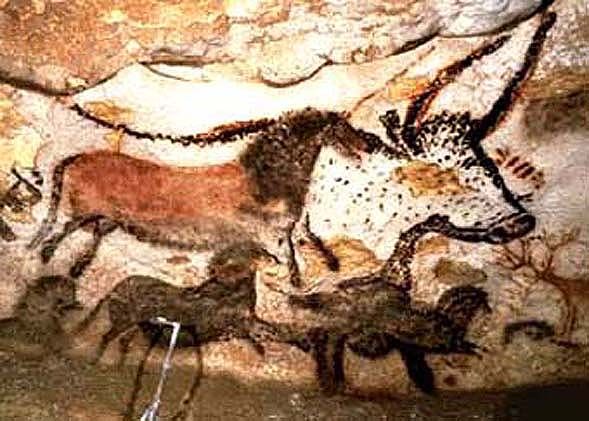
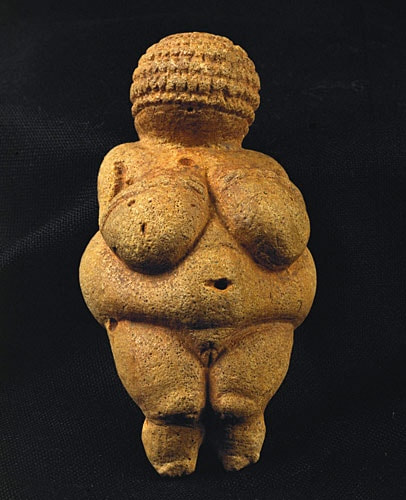
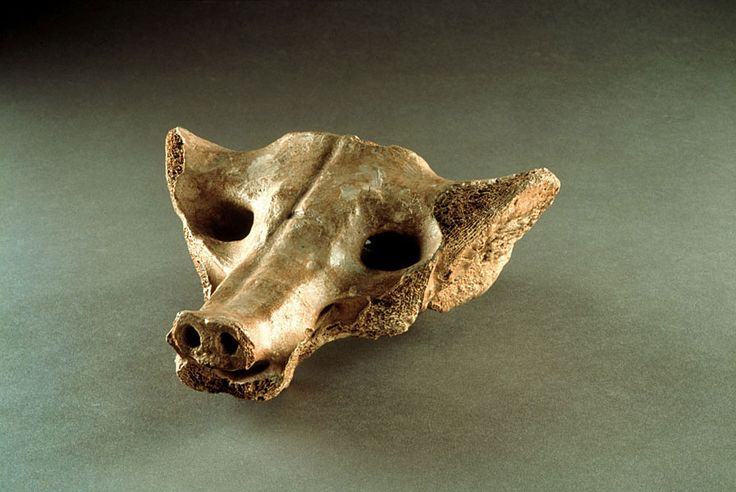
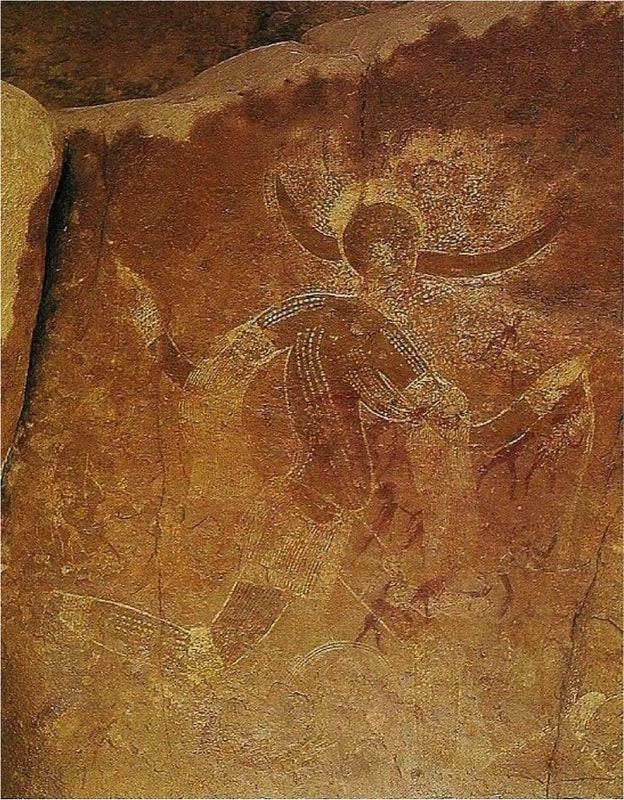
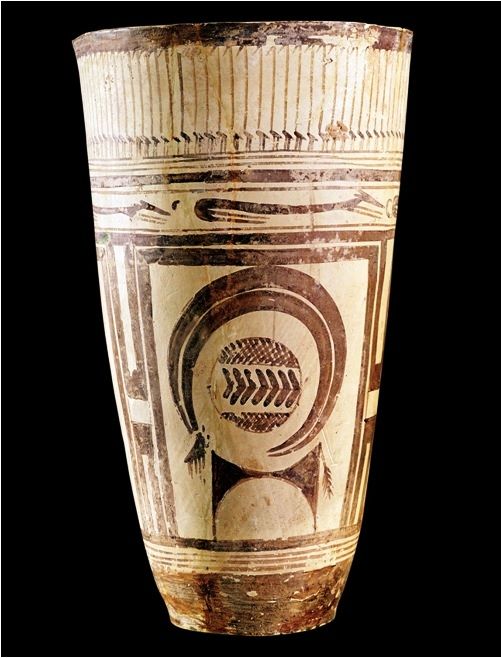
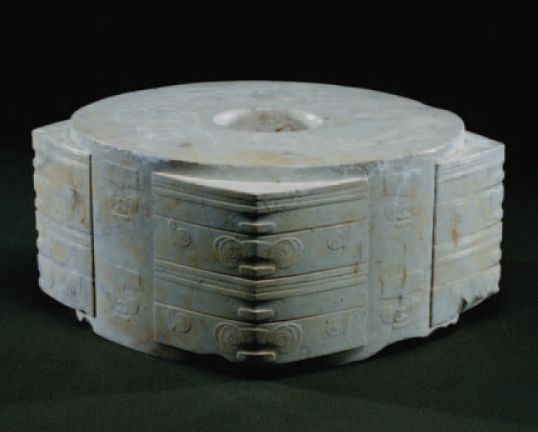
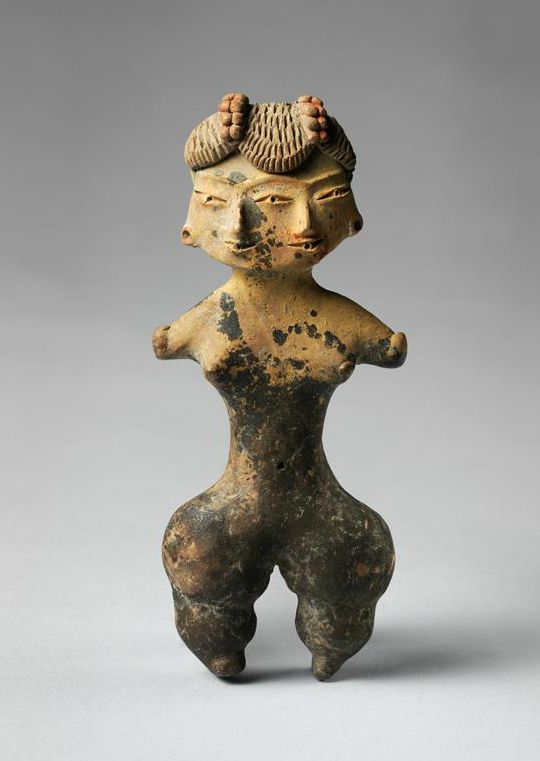
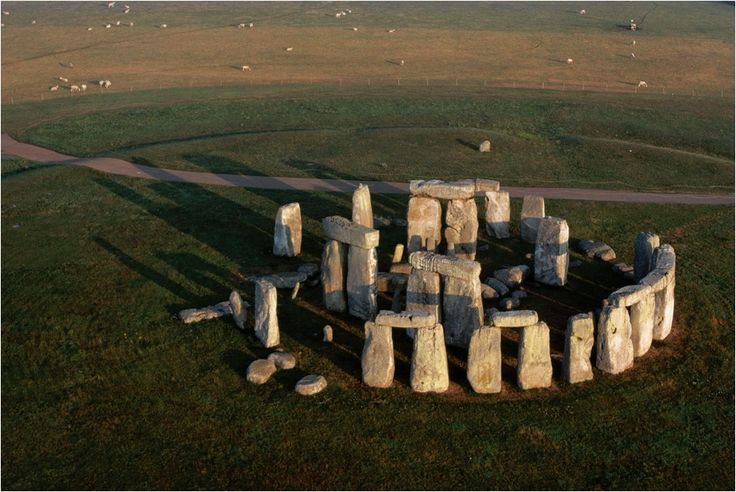
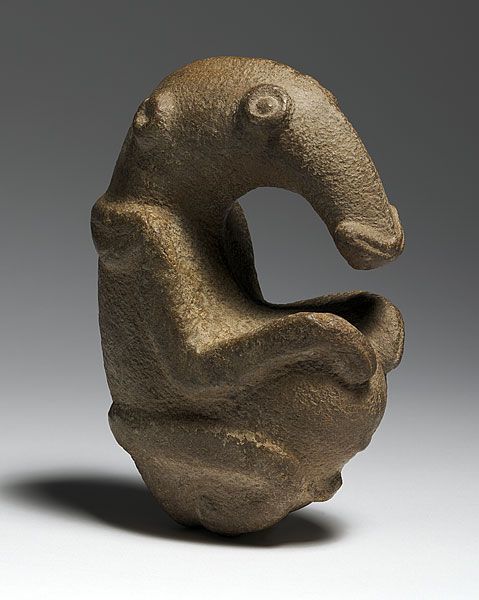
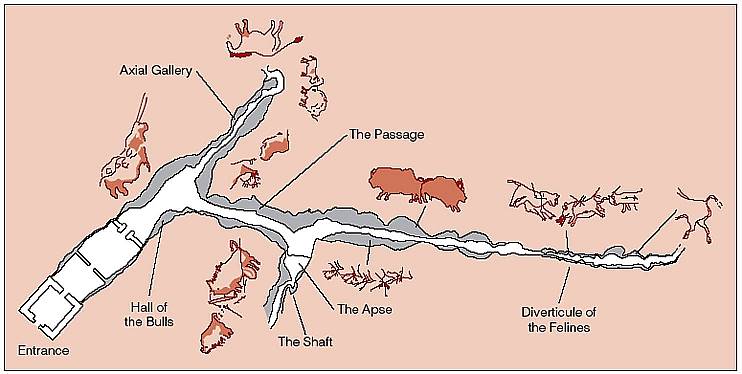
2. Great Hall of the Bulls 3. Camelid sacrum in the shape of a canine 4. Running Horned Woman 5. Beaker with Ibex motifs 6. Anthropomorphic stele 7. Jade cong 8. Stonehenge 9. The Ambum stone 10. Tlatilco female figurine 11. Terra cotta fragment Extra image: Venus of Willendorf NEED TO KNOW DATES...Paleolithic Art: 40,000-8,000 BCE in the Near East
"Old Stone Age" 40,000-4,000 BCE in Europe (Woman of Willendorf, Feline-headed statue, Lascaux Caves, Catal Hoyuk)
Neolithic Art: 8,000- 3,000 BCE in the Near East "New Stone Age" 4,000- 2,000 BCE in Europe (Stonehenge)
|
KEY IDEAS
|
CHARACTERISTICS OF
|
CHARACTERISTICS OF
|
CHARACTERISTICS OF
|
CONTEXT |
|
Ritual and symbolic works might have encouraged the availability of food sources. The first art-making was associated with activities of food production (hunting, agriculture, etc.), showing status, and burial.
Artifacts show human's awareness of fundamental, stable situations/experiences/incidents from astrological events to manipulation of materials available. Art production was used to connect and influence the natural world to human needs - sustaining life, and fertility. Animal images and female figuresseem to be connected to shamanistic rituals. Due to the absence of written records and other contextual information, there is a lack of certainty regarding prehistoric artifacts. Multiple interpretations are presented due toarchaeological and ethnographic (study of human cultures) approaches of function and meaning of the works of art. |
VOCABULARY
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|